AI in HR: Keeping the “Human” in Human Resources
With the release of ChatGPT in November 2022, the world feels like a completely new landscape. AI-generated text, poetry, music, art, video, characters, and chats abound. AI is rapidly changing the way we work, play, and live. And while it’s not new (AI assistants like Siri and Alexa; algorithmic suggestions; and even navigation apps are all well-accepted uses of AI), the rapid changes as AI grows can feel unsettling.
How should human resources respond, both to AI implemented in workplace practices and to the potential for use of AI in HR?
Check your company policies. According to SHRM, 78% of HR departments have no policies around the use of AI (2024). This is a huge problem when you consider that generative, deep learning networks like ChatGPT store data that it’s fed. What happens if confidential client information, or HIPAA, FERPA, or other legally-protected information is fed into the machine? Be clear about what can and cannot be put into AI.
Use AI to streamline HR functions. Generative AI can take over a lot of administrative HR functions, like updating job descriptions, writing offer letters, and drafting email and company-wide correspondence. You need to check the output of course. ChatGPT (by OpenAI) and Gemini (by Google) warn users that AI produces incorrect responses regularly.
Consult your legal team, especially if using AI for recruiting. AI can screen resumes and be invaluable for high-volume applicant roles. However, you have to remember that AI learns from the data it’s been fed. For example, when it was audited in 2015, Amazon’s AI screening program was discovered to prefer male applicants. Because it was trained on the past 10 years of accepted tech candidates in a male-dominated field, it learned to prefer male resumes (with male-connotative language like “achieve” or “compete”) and screen against female resumes (with the words “women” or “women’s) (Goodman, 2018).
Remember who is liable for the robot. You, employer, are liable for discrimination committed by AI. A tutoring company paid $365,000 after investigations revealed the AI screened against applicants over 55 years old, who are protected by the Age Discrimination in Employment Act (ADEA) (Fisher Phillips, 2023).
We share this, not to scare you, but to keep you informed. AI is powerful and like any tool, can create chaos or harmony in your organization. See below some examples of prompts we fed into AI to generate job descriptions, cover letters, and employee schedules.
Prompt: “Update this job description: [Paste job description text]
And emphasize the need for strong oral and written community skills, and a dynamic presence, for sales and outreach efforts.”
Output: (from ChatGPT)
Prompt: These staff are available to work on these days: [Enter staff]
These are my shifts: [enter shifts]
Create a schedule that ensures no one works more than 40 hours per week.”
Output: (from ChatGPT)
Prompt: “Write a performance improvement plan for Jill who has failed to turn in 8 assignments on time as assigned and has not met her weekly call quota of 300 cold sales calls per week.”
Output: (from Google Gemini)
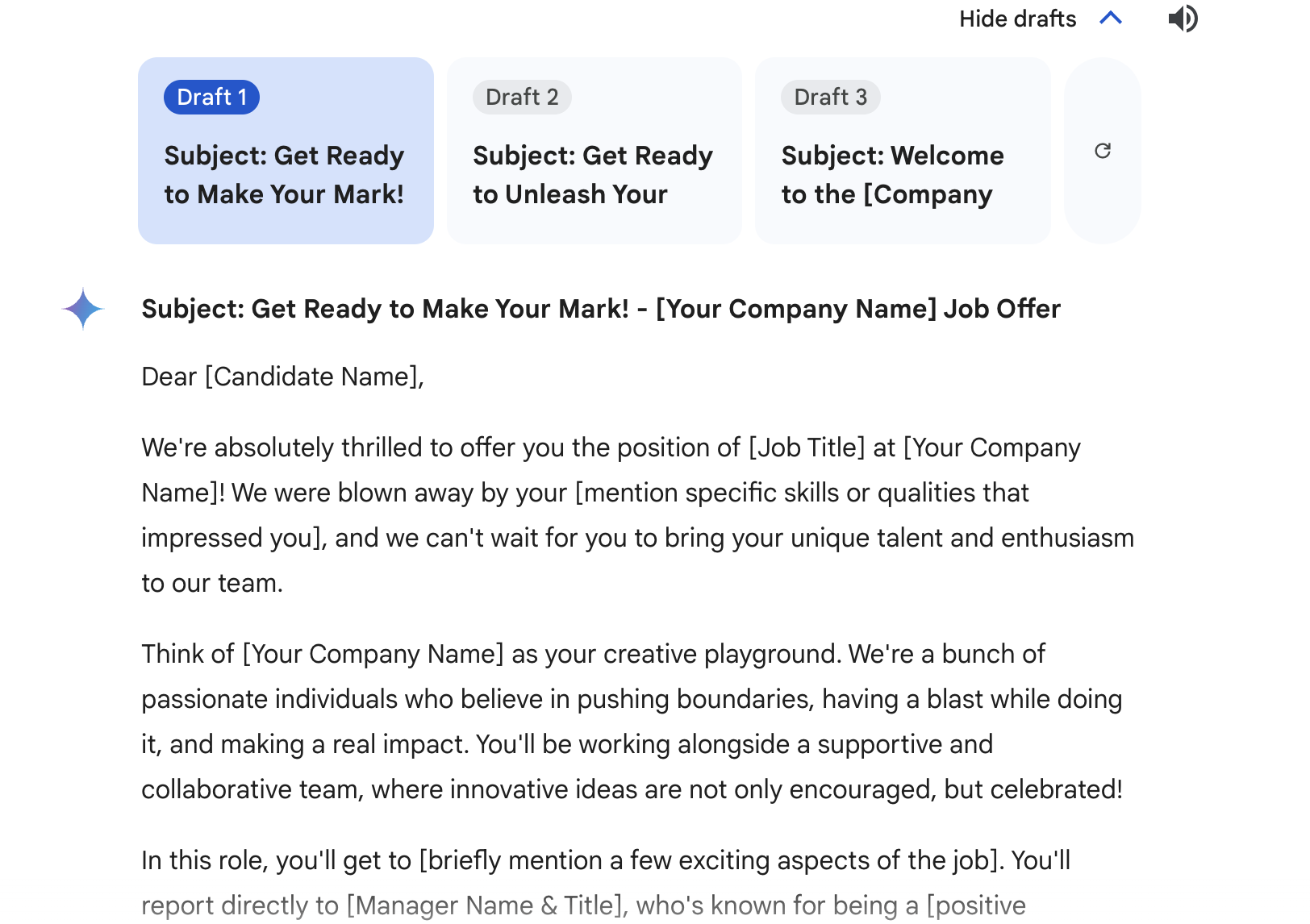
Prompt: “Draft an offer letter to a candidate who will be making $60,000 per year, in our office. Reflect our company's fun and innovative culture in the tone!”
Output: (from Google Gemini)
References
Fisher Phillips. (2023, Aug 14). EEOC Breaks New Ground by Settling First-Ever AI Discrimination Lawsuit: 10 Pointers to Avoid Robot Bias. Fisher Phillips. https://www.fisherphillips.com/en/news-insights/eeoc-ai-discrimination-lawsuit-10-pointers.html
Goodman, Rachel. (2018, Oct 12). ACLU. Why Amazon’s Automated Hiring Tool Discriminated Against Women. ACLU. https://www.aclu.org/news/womens-rights/why-amazons-automated-hiring-tool-discriminated-against
Iriondo, Robert. (2018, Oct 11). Amazon Scraps Secret AI Recruiting Engine that Showed Biases Against Women. Carnegie Mellon University. Brown, Sara. (2021, Apr 21). Machine learning, explained. MIT Sloan School of Management. https://mitsloan.mit.edu/ideas-made-to-matter/machine-learning-explained
Society for Human Resource Management. (2024). AI in the workplace: a SHRM guide to human-centered AI adoption in the workplace. SHRM.